This guide will take you through how to setup OpenLDAP server with SSL/TLS on Debian 10 Buster. OpenLDAP clients and servers are capable of using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) framework to provide integrity and confidentiality protections and to support LDAP authentication using the SASL EXTERNAL mechanism.
Setup OpenLDAP Server with SSL/TLS on Debian 10
Update and upgrade your system packages
apt update
apt upgradeInstall LDAP packages
apt -y install slapd ldap-utils ldapscriptsDuring the installation, you are prompted to set the LDAP admin password.
Re-enter the password to verify it and press Enter to continue.
View LDAP Database Settings
During the installation, the LDAP database is automatically setup with the distinguished name’s (DN) domain component, organization name being set based on the default system hostname. To view the SLAPD database settings, you can use the slapcat command.
slapcatdn: dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
objectClass: top
objectClass: dcObject
objectClass: organization
o: kifarunix-demo.com
dc: kifarunix-demo
structuralObjectClass: organization
entryUUID: d659c794-5ffd-1039-84a2-a3c9b919ad9c
creatorsName: cn=admin,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
createTimestamp: 20190831054217Z
entryCSN: 20190831054217.507918Z#000000#000#000000
modifiersName: cn=admin,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
modifyTimestamp: 20190831054217Z
dn: cn=admin,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
objectClass: simpleSecurityObject
objectClass: organizationalRole
cn: admin
description: LDAP administrator
userPassword:: e1NTSEF9TkpLYnEvUG1TRi9rUFdJTVlMbjF0UjF3SC9YWWV1ZUo=
structuralObjectClass: organizationalRole
entryUUID: d65a43a4-5ffd-1039-84a3-a3c9b919ad9c
creatorsName: cn=admin,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
createTimestamp: 20190831054217Z
entryCSN: 20190831054217.511167Z#000000#000#000000
modifiersName: cn=admin,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
modifyTimestamp: 20190831054217ZBased on the SLAPD database configuration output above,
- The Base DN is set to
dn: dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com. - The Organization name is set to
o: kifarunix-demo.com. - The LDAP admin Base DN entry is set to
dn: cn=admin,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com.
Change OpenLDAP Default BaseDN
If you however need the default OpenLDAP base DN, you need to reconfigure slapd package as shown below and follow through the prompts.
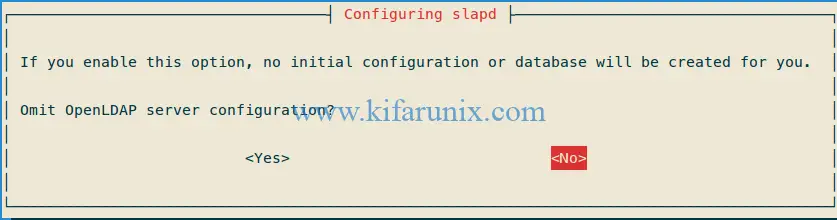
dpkg-reconfigure slapdWhen the command runs, you are prompted on whether to omit OpenLDAP server configuration. Select No to have the configuration created for you.
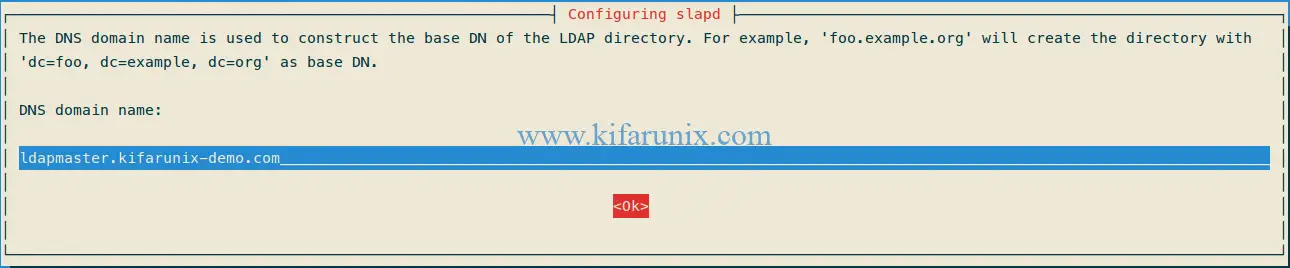
Next, configure your OpenLDAP server fully qualified domain name that will be used to create your Base DN.
Set the name of your organization. You can use the domain name.
Set and verify the Admin pass.
Select the OpenLDAP database backend. MDB is the recommended type. Select MDB and proceed.
Select whether you want the slapd database removed when you uninstall it.
Remove old OpenLDAP database configuration files to finalize the reconfiguration. The old database is stored on /var/backups.
To verify the reconfiguration, simply execute slapcat command.
slapcatdn: dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
objectClass: top
objectClass: dcObject
objectClass: organization
o: kifarunix-demo.com
dc: ldapmaster
structuralObjectClass: organization
entryUUID: 8086d846-602c-1039-9746-f9b0ac2d943e
creatorsName: cn=admin,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
createTimestamp: 20190831111619Z
entryCSN: 20190831111619.865416Z#000000#000#000000
modifiersName: cn=admin,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
modifyTimestamp: 20190831111619Z
dn: cn=admin,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
objectClass: simpleSecurityObject
objectClass: organizationalRole
cn: admin
description: LDAP administrator
userPassword:: e1NTSEF9dFY4Y01CRXI3OExPOFZNTnoyeGFHdGlySkxPNEQxdHM=
structuralObjectClass: organizationalRole
entryUUID: 8087b7b6-602c-1039-9747-f9b0ac2d943e
creatorsName: cn=admin,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
createTimestamp: 20190831111619Z
entryCSN: 20190831111619.871279Z#000000#000#000000
modifiersName: cn=admin,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
modifyTimestamp: 20190831111619ZYou can also check LDAP Base DN using the ldapsearch command as shown below;
ldapsearch -H ldapi:/// -x -LLL -s base -b "" namingContextsdn:
namingContexts: dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=comTo view the RootDN, run the command below
ldapsearch -H ldapi:/// -Y EXTERNAL -b "cn=config" "(olcRootDN=*)"To test the connection to LDAP server, use the ldapwhoami command as shown below.
ldapwhoami -H ldapi:/// -xanonymousThe expected output is anonymous if the connection to LDAP server is fine since the test is run without logging in to LDAP server.
To search for all the DNs based on the Base DN;
ldapsearch -H ldapi:/// -x -LLL -b dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com dndn: dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
dn: cn=admin,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=comCreate a Base DN for Users and Groups
From the SLAPD database configuration output above, the Base DN for the OpenLDAP admin has been created. However, since we are going to manage other users apart from the LDAP administrator, you need to create a Base DN for users and groups.
Therefore create an LDAP interchange format file (ldif) with the following contents and use it to create the user/group Base DN. Be sure to replace the domain name accordingly.
vim user_group_base.ldifdn: ou=people,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
objectClass: organizationalUnit
ou: people
dn: ou=group,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
objectClass: organizationalUnit
ou: groupAdd Users and Groups Base DN to SLAPD database
Once you have created an ldif file for users and groups base DN, you can populate the slapd database with this information using the ldapadd command as shown below;
ldapadd -x -D cn=admin,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com -W -f user_group_base.ldifWhen prompted, enter the LDAP admin password set above.
Enter LDAP Password: admin password
adding new entry "ou=people,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com"
adding new entry "ou=group,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com"Create LDAP User Accounts
In order to add LDAP user accounts to LDAP Server, you need to create an LDIF file containing attributes definition for the users.
To add user with a password, you need to generate the user’s password hash using the slappasswd command.
slappasswdNew password: USER_PASS
Re-enter new password: RE_ENTER USER_PASS
{SSHA}sO8V/PZsGCta6098vs2qgX767AJF3Sw7You can as well create user password using the ldappasswd command after creating the user. See the section below on Resetting user password.
Next, create new user ldif file containing attributes definition for the user as shown below.
vim new_user.ldifdn: uid=mibeyam,ou=people,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
objectClass: inetOrgPerson
objectClass: posixAccount
objectClass: shadowAccount
uid: mibeyam
cn: mibeyam
givenName: Amos
sn: Mibey
userPassword: {SSHA}sO8V/PZsGCta6098vs2qgX767AJF3Sw7
loginShell: /bin/bash
uidNumber: 10000
gidNumber: 10000
homeDirectory: /home/mibeyam
shadowMax: 60
shadowMin: 1
shadowWarning: 7
shadowInactive: 7
shadowLastChange: 0
dn: cn=mibeyam,ou=group,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
objectClass: posixGroup
cn: mibeyam
gidNumber: 10000
memberUid: mibeyamAdd Users to SLAPD database
Once you have created the users with their attributes in an LDIF file, you can add them to the database using the ldapadd command.
ldapadd -x -D cn=admin,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com -W -f new_user.ldifWhen prompted, enter LDAP admin password.
Enter LDAP Password: admin password
adding new entry "uid=mibeyam,ou=people,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com"
adding new entry "cn=mibeyam,ou=group,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com"To list all LDAP users under a base DN, simply use the ldapsearch command.
ldapsearch -x -LLL -b "dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com"dn: dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
objectClass: top
objectClass: dcObject
objectClass: organization
o: kifarunix-demo.com
dc: ldapmaster
dn: cn=admin,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
objectClass: simpleSecurityObject
objectClass: organizationalRole
cn: admin
description: LDAP administrator
dn: ou=people,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
objectClass: organizationalUnit
ou: people
dn: ou=group,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
objectClass: organizationalUnit
ou: group
dn: uid=mibeyam,ou=people,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
objectClass: inetOrgPerson
objectClass: posixAccount
objectClass: shadowAccount
uid: mibeyam
cn: mibeyam
givenName: Amos
sn: Mibey
loginShell: /bin/bash
uidNumber: 10000
gidNumber: 10000
homeDirectory: /home/mibeyam
shadowMax: 60
shadowMin: 1
shadowWarning: 7
shadowInactive: 7
shadowLastChange: 0
dn: cn=mibeyam,ou=group,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
objectClass: posixGroup
cn: mibeyam
gidNumber: 0
memberUid: mibeyamTo list specific attributes from the objectClass,
ldapsearch -x -LLL -b "dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com" '(objectclass=*)' uid givenName snThis will print the user id, given names and surnames. Of course you can pass the output to text processing tools like grep to extract the attributes you need.
ldapsearch -x -LLL -b "dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com" '(objectclass=*)' uid givenName sn | grep -vE 'uid=|dn:'uid: mibeyam
givenName: Amos
sn: Mibey
uid: johndo
givenName: John
sn: DoeDelete LDAP Users and Groups
To delete an LDAP user, use the ldapdelete command. For example do delete mibeyam user created above
ldapdelete -x -W -D "cn=admin,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com" "uid=mibeyam,ou=people,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com"Similarly, to delete an LDAP user group;
ldapdelete -x -W -D "cn=admin,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com" "cn=mibeyam,ou=group,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com"Resetting LDAP User Password
If you need to reset the user password, you can use ldappasswd command. For example, to reset the password for user mibeyam;
ldappasswd -H ldapi:/// -x -D "cn=admin,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com" -W -S "uid=mibeyam,ou=people,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com"If you are connecting to LDAP server from a remote client, ensure that open OpenLDAP on firewall. If UFW is running;
ufw allow ldapTo connect remotely, ensure that you use the -H ldap://<ldap-server-IP> option. For example;
ldappasswd -H ldap://192.168.56.105 -x -D "cn=admin,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com" -W -S "uid=mibeyam,ou=people,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com"Verify LDAP User Password
To verify that password assigned to an LDAP user is working, use the ldapwhoami command. For example to verify the password for the user mibeyam,
ldapwhoami -vvv -h localhost -D "uid=mibeyam,ou=people,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com" -x -WIf the password is correct, you will get an output similar to this;
ldap_initialize( ldap://localhost )
Enter LDAP Password:
dn:uid=mibeyam,ou=people,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com
Result: Success (0)To test from remote client;
ldapwhoami -vvv -h LDAP-SERVER-IP-OR-HOSTNAME -D "uid=mibeyam,ou=people,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com" -x -WReplace LDAP-SERVER-IP-OR-HOSTNAME with LDAP server IP or resolvable hostname.
Configure OpenLDAP with SSL/TLS
Generate SSL/TLS certificates
In this guide, we are going to use self signed certificates. You can as well use commercial SSL/TLS certificates from your trusted CA.
To configure OpeLDAP server with SSL/TLS certificate, you need a CA certificate, server certificate and server certificate key file.
Create a directory to store the certificates.
mkdir -p /etc/ssl/openldap/{private,certs,newcerts}Once you have created the directories above, open the /usr/lib/ssl/openssl.cnf configuration file and set the directory for storing SSL/TLS certificates and keys under the [ CA_default ] section.
vim /usr/lib/ssl/openssl.cnf...
[ CA_default ]
#dir = ./demoCA # Where everything is kept
dir = /etc/ssl/openldap
certs = $dir/certs # Where the issued certs are kept
crl_dir = $dir/crl # Where the issued crl are kept
database = $dir/index.txt # database index file.
...You also need some files for tracking the signed certificates.
echo "1001" > /etc/ssl/openldap/serialtouch /etc/ssl/openldap/index.txtCreate a CA Key file by running the command below. When prompted, enter the passphrase.
openssl genrsa -aes256 -out /etc/ssl/openldap/private/cakey.pem 2048To remove the passphrase from the CA key;
openssl rsa -in /etc/ssl/openldap/private/cakey.pem -out /etc/ssl/openldap/private/cakey.pemCreate the CA certificate. Be sure to set the common to match your server FQDN.
openssl req -new -x509 -days 3650 -key /etc/ssl/openldap/private/cakey.pem -out /etc/ssl/openldap/certs/cacert.pemNext generate LDAP server key;
openssl genrsa -aes256 -out /etc/ssl/openldap/private/ldapserver-key.key 2048Remove assigned key passphrase.
openssl rsa -in /etc/ssl/openldap/private/ldapserver-key.key -out /etc/ssl/openldap/private/ldapserver-key.keyGenerate the certificate signing request (CSR). Be sure to configure the same details as you did when generating the CA certificate file above.
openssl req -new -key /etc/ssl/openldap/private/ldapserver-key.key -out /etc/ssl/openldap/certs/ldapserver-cert.csrGenerate the LDAP server certificate and sign it with CA key and certificate generated above.
openssl ca -keyfile /etc/ssl/openldap/private/cakey.pem -cert /etc/ssl/openldap/certs/cacert.pem -in /etc/ssl/openldap/certs/ldapserver-cert.csr -out /etc/ssl/openldap/certs/ldapserver-cert.crtTo verify the LDAP server againt the CA;
openssl verify -CAfile /etc/ssl/openldap/certs/cacert.pem /etc/ssl/openldap/certs/ldapserver-cert.crt/etc/ssl/openldap/certs/ldapserver-cert.crt: OKNow, we have the CA certificate file, the server certificate and the server key file under the following respective directories.
/etc/ssl/openldap/certs/cacert.pem/etc/ssl/openldap/certs/ldapserver-cert.crt/etc/ssl/openldap/private/ldapserver-key.keyNext, set the ownership of the OpenLDAP certificates directory to openldap user.
chown -R openldap: /etc/ssl/openldap/Update OpenLDAP Server TLS Certificates
Next, you need to update the OpenLDAP Server TLS certificates. Therefore, create the an LDIF file to define the TLS attributes as shown below;
vim ldap-tls.ldifdn: cn=config
changetype: modify
add: olcTLSCACertificateFile
olcTLSCACertificateFile: /etc/ssl/openldap/certs/cacert.pem
-
replace: olcTLSCertificateFile
olcTLSCertificateFile: /etc/ssl/openldap/certs/ldapserver-cert.crt
-
replace: olcTLSCertificateKeyFile
olcTLSCertificateKeyFile: /etc/ssl/openldap/private/ldapserver-key.key
Replace the locations of your certificates and key files accordingly.
To modify these entries on the LDAP database, use ldapmodify command as shown below;
ldapmodify -Y EXTERNAL -H ldapi:/// -f ldap-tls.ldifSASL/EXTERNAL authentication started
SASL username: gidNumber=0+uidNumber=0,cn=peercred,cn=external,cn=auth
SASL SSF: 0
modifying entry "cn=config"To verify that the files are in place;
slapcat -b "cn=config" | grep -E "olcTLS"olcTLSCACertificateFile: /etc/ssl/openldap/certs/cacert.pem
olcTLSCertificateFile: /etc/ssl/openldap/certs/ldapserver-cert.crt
olcTLSCertificateKeyFile: /etc/ssl/openldap/private/ldapserver-key.keyTo check the validity of the LDAP configuration, run the command below;
slaptest -uconfig file testing succeededNext, open the /etc/ldap/ldap.conf configuration file and change the location of the CA certificate.
vim /etc/ldap/ldap.conf...
# TLS certificates (needed for GnuTLS)
#TLS_CACERT /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
TLS_CACERT /etc/ssl/openldap/certs/cacert.pemRestart OpenLDAP daemon.
systemctl restart slapdVerify TLS connectivity for LDAP
To verify OpenLDAP TLS connectivity, run the command below. If connection is fine, you should get the output, anonymous.
ldapwhoami -H ldap://ldapmaster.kifarunix-demo.com -x -ZZ
anonymousldapwhoami -H ldapi:/// -x -ZZ
anonymousDisable Anonymous OpenLDAP Access
To disable anonymous OpenLDAP access such that you need to authenticate to be able to access LDAP;
vim disable-anon.ldifdn: cn=config
changetype: modify
add: olcDisallows
olcDisallows: bind_anon
dn: cn=config
changetype: modify
add: olcRequires
olcRequires: authc
dn: olcDatabase={-1}frontend,cn=config
changetype: modify
add: olcRequires
olcRequires: authcUpdate slapd database;
ldapadd -Y EXTERNAL -H ldapi:/// -f disable-anon.ldifTest anonymous authentication.
ldapwhoami -H ldapi:/// -x -ZZldap_bind: Inappropriate authentication (48)
additional info: anonymous bind disallowedTest Authentication
ldapwhoami -H ldapi:/// -x -ZZ -D "uid=mibeyam,ou=people,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=com" -x -WEnter LDAP Password:
dn:uid=mibeyam,ou=people,dc=ldapmaster,dc=kifarunix-demo,dc=comConfigure OpenLDAP Logging
Configure OpenLDAP to log to a specific log file. First, enable OpenLDAP to log connections, operations, results statistics. Such logging is enable on log level 256 with keyword stats. This can be done by modifying the olcLogLevel attribute as shown below.
vim enable-ldap-log.ldifdn: cn=config
changeType: modify
replace: olcLogLevel
olcLogLevel: statsldapmodify -Y external -H ldapi:/// -f enable-ldap-log.ldifSASL/EXTERNAL authentication started
SASL username: gidNumber=0+uidNumber=0,cn=peercred,cn=external,cn=auth
SASL SSF: 0
modifying entry "cn=config"ldapsearch -Y EXTERNAL -H ldapi:/// -b cn=config "(objectClass=olcGlobal)" olcLogLevel -LLLSASL/EXTERNAL authentication started
SASL username: gidNumber=0+uidNumber=0,cn=peercred,cn=external,cn=auth
SASL SSF: 0
dn: cn=config
olcLogLevel: statsConfigure Rsyslog to enable OpenLDAP to log to a specific file. By default, OpenLDAP logs to local4 facility.
echo "local4.* /var/log/slapd.log" >> /etc/rsyslog.confRestart Rsyslog
systemctl restart rsyslogRestart LDAP server service.
systemctl restart slapdYou can now read the log file, /var/log/slapd.log.
So far so good, we have learnt how to setup OpenLDAP Server with SSL/TLS on Debian 10. In our next guides, we will learn how to configure LDAP clients to authenticate via LDAP Server.
Related Tutorials
Install and Configure OpenLDAP Server on Debian 9 Stretch


When I did
ldapmodify -Y EXTERNAL -H ldap:/// -f ldap-tls.ldif
I Got :-
SASL/EXTERNAL authentication started
ldap_sasl_interactive_bind_s: Unknown authentication method (-6)
additional info: SASL(-4): no mechanism available:
I think we will need also TLS_REQCERT allow
“`
…
# TLS certificates (needed for GnuTLS)
#TLS_CACERT /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
TLS_CACERT /etc/ssl/openldap/certs/cacert.pem
TLS_REQCERT allow
“`
after running ldapmodify -Y EXTERNAL -H ldapi:/// -f ldap-tls.ldif
i get the error ldap_modify: Other (e.g., implementation specific) error (80)
how can i go pass this
I have the same issue
Hello Suvin,
What is the ownership of the certs and key file?
openldap is the owner
Add these lines to /etc/apparmor.d/usr.sbin.slapd if you have apparmor:
/etc/ssl/openldap/certs/* r,
/etc/ssl/openldap/private/* r,
That will fix one cause of ldap_modify: Other (e.g., implementation specific) error (80)
very very great tutorial !
thank you
I need some direction in creating the certificates. When I originally installed OpenLDAP I set the FQDN to (slapdomain.local) in the configuration wizard. My Ubuntu 20.04 server’s hostname is (ulogin). When generating the SSL/TLS certificates, which of the following should I use?
ulogin.slapdomain.local
slapdomain.local
I went through the entire process having used (slapdomain.local) for the certificates, and all went really well until I got to the part where I was checking the user’s password. I think this is because this command is the first one in the tutorial that references the server by name. I’ve tried the following commands:
ldapwhoami -h ldap.sladomain.local -x -D “uid=joebob,ou=people,dc=slapdomain,dc=local” -W
ldapwhoami -h ldap.sladomain.local -x -D “uid=joebob,ou=people,dc=slapdomain,dc=local” -W
…and I receive the following error:
ldap_sasl_bind(SIMPLE): Can’t contact LDAP server (-1)
I’m guessing this is a TLS/SSL certificate name mis-match problem, but am not sure. I am doing this for a class and we haven’t learned any of this at all. We are actually just learning PAM, and the object of the assignment it to create a working central login server.
Any help would be greatly appreciated.
I sincerely apologize, I pasted the commands incorrectly:
ldapwhoami -h ldap.slapdomain.local -x -D “uid=joebob,ou=people,dc=slapdomain,dc=local” -W
ldapwhoami -h slapdomain.local -x -D “uid=joebob,ou=people,dc=slapdomain,dc=local” -W
Both return:
ldap_sasl_bind(SIMPLE): Can’t contact LDAP server (-1)
Certificate FQDN is: slapdomain.local
I am able to set the password just fine, but I believe that is because I am using ldapi:/// in the command instead of the server’s name.
Again, thank you.
Make sure you have an entry for ulogin.slapdomain.local in /etc/hosts and then use that for the FQDN on the cert. You don’t necessarily want to put just “slapdomain.local” in hosts if you’re going to have other machines in the domain. If you had a wildcard cert for *.slapdomain.local you could use that, too, but it’s probably easier to just go through the instructions here again with the correct FQDN.
Is there any reason why the user/group OUs are named “people” and “group” rather than “users” and “groups” or is this simply personal preference?
Also I see in this tutorial (for Debian 10) that “group” (singular) is used but in the Ubuntu 20.04 tutorial on your site “groups” (plural) is used
You can define your own OU.
Personal preference.
chown -R openldap: /etc/ssl/openldap/
ERROR:
chown: invalid spec: ‘openldap:’