In this guide, you will learn how to install GVM 21.4 on Ubuntu 20.04. Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM), previously known as OpenVAS, is a network security scanner which provides a set of network vulnerability tests (NVTs) to detect security loopholes in systems and applications. As of this writing, GVM 21.4 is the current stable release and is the latest release.
Install GVM 21.4 on Ubuntu 20.04
Prerequisites
In this demo, we will install and setup GVM 21.4 on Ubuntu 20.04 from source code. As such, below are the system requirements I would personally recommend.
- At least 4 GB RAM
- At least 4 vCPUs
- More than 8 GB disk space (We used 16 GB in this demo)
These requirements will vary depending on your use cases, however. Just be sure to provide “enough”.
Run System Update
To begin with, update your system package cache and upgrade your system packages;
apt updateCreate GVM User on Ubuntu
In this demo, we will run GVM 21.4 as a non privileged system user. Thus, create gvm system user account.
useradd -r -m -d /opt/gvm -c "GVM User" -s /bin/bash gvmInstall Required Build Tools
In order to successfully build GVM 21.4 on Ubuntu 20.04, you need to install a number of required dependencies and build tools.
apt install gcc g++ make bison flex libksba-dev curl redis libpcap-dev \
cmake git pkg-config libglib2.0-dev libgpgme-dev nmap libgnutls28-dev uuid-dev \
libssh-gcrypt-dev libldap2-dev gnutls-bin libmicrohttpd-dev libhiredis-dev \
zlib1g-dev libxml2-dev libradcli-dev clang-format libldap2-dev doxygen libnet1-dev \
gcc-mingw-w64 xml-twig-tools libical-dev perl-base heimdal-dev libpopt-dev \
libsnmp-dev python3-setuptools python3-paramiko python3-lxml python3-defusedxml \
python3-dev gettext python3-polib xmltoman python3-pip texlive-fonts-recommended \
texlive-latex-extra --no-install-recommends xsltproc libunistring-dev vim -y
Install Yarn on Ubuntu 20.04
Next, install Yarn JavaScript package manager
curl -sS https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/pubkey.gpg | gpg --dearmor > /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/yarn.gpgecho "deb https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/ stable main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/yarn.listapt updateapt install yarn -yInstall PostgreSQL on Ubuntu 20.04
GVM 21.4 uses PostgreSQL as the backend database.
Therefore, run the command below to install PostgreSQL on Ubuntu 20.04;
apt install postgresql postgresql-contrib postgresql-server-dev-allStart and enable PostgreSQL to run on system boot;
systemctl enable --now postgresqlCreate PostgreSQL User and Database
Once the installation is done, create the PostgreSQL user and database for Greenbone Vulnerability Management Daemon (gvmd). Note that the database and user should be created as PostgreSQL user, postgres.
sudo -Hiu postgres createuser gvmsudo -Hiu postgres createdb -O gvm gvmdGrant PostgreSQL GVM User DBA Roles
sudo -Hiu postgres psql gvmd -c 'create role dba with superuser noinherit;'sudo -Hiu postgres psql gvmd -c 'grant dba to gvm;'sudo -Hiu postgres psql gvmd -c 'create extension "uuid-ossp";'sudo -Hiu postgres psql gvmd -c 'create extension "pgcrypto";'Once that is done, restart PostgreSQL;
systemctl restart postgresqlBuilding GVM 21.4 from Source Code
There are different tools required to install and setup GVM 21.4 on Ubuntu 20.04. These include;
- GVM Libraries
- OpenVAS Scanner
- OSPd
- ospd-openvas
- Greenbone Vulnerability Manager
- Greenbone Security Assistant
- Python-GVM
- GVM-Tools
- OpenVAS SMB
Every component has README.md and a INSTALL.md file that explains how to build and install it.
Since we are running GVM as non-privileged user, gvm, then we will install all the GVM configuration files and libraries under, /opt/gvm (/opt/gvm/bin:/opt/gvm/sbin:/opt/gvm/.local/bin).
Update the PATH environment variable on /etc/environment, to include the GVM binary path such that it looks like;
sed -i.bak '/^PATH/s|"$|:/opt/gvm/bin:/opt/gvm/sbin:/opt/gvm/.local/bin"|' /etc/environmentsource /etc/environmentAdd GVM library path to /etc/ld.so.conf.d.
echo "/opt/gvm/lib" > /etc/ld.so.conf.d/gvm.confBuild and Install GVM on Ubuntu 20.04
Before you can proceed, enable gvm user to run installation command with sudo rights;
echo "gvm ALL = NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/make install" >> /etc/sudoers.d/gvmSwitch to GVM user, gvm and create a temporary directory to store GVM source files.
sudo -Hiu gvm mkdir gvm-sourceDownload GVM 21.4 Source Files
Clone the GVM github branch files into directory created above.
sudo -Hiu gvm git clone -b stable --single-branch https://github.com/greenbone/gvm-libs.git gvm-source/gvm-libssudo -Hiu gvm git clone -b main --single-branch https://github.com/greenbone/openvas-smb.git gvm-source/openvas-smbsudo -Hiu gvm git clone -b stable --single-branch https://github.com/greenbone/openvas.git gvm-source/openvassudo -Hiu gvm git clone -b stable --single-branch https://github.com/greenbone/ospd.git gvm-source/ospdsudo -Hiu gvm git clone -b stable --single-branch https://github.com/greenbone/ospd-openvas.git gvm-source/ospd-openvassudo -Hiu gvm git clone -b stable --single-branch https://github.com/greenbone/gvmd.git gvm-source/gvmdsudo -Hiu gvm git clone -b stable --single-branch https://github.com/greenbone/gsa.git gvm-source/gsasudo -Hiu gvm git clone -b stable --single-branch https://github.com/greenbone/gsad.git gvm-source/gsadThe source files are in now place;
ls -1 /opt/gvm/gvm-sourcels -1gsa
gsad
gvm-libs
gvmd
openvas
openvas-smb
ospd
ospd-openvas
Note that we will install all GVM 21.4 files and libraries to a non-standard location, /opt/gvm.
Switch to GVM user;
su - gvmAs such, you need to set the PKG_CONFIG_PATH environment variable to the location of your pkg-config files before configuring:
echo "export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/opt/gvm/lib/pkgconfig:$PKG_CONFIG_PATH" >> ~/.bashrcsource ~/.bashrcBe sure to replace the path, /opt/gvm, accordingly.
Build and Install GVM Libraries
From within the source directory, /opt/gvm/gvm-source, in this setup, change to GVM libraries directory;
cd ~/gvm-source/gvm-libsCreate a build directory and change into it;
mkdir build && cd buildConfigure the build;
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/gvmNext, compile and install GVM libraries
make && sudo make installBuild and Install OpenVAS scanner and OpenVAS SMB
Open Vulnerability Assessment Scanner (OpenVAS) is a full-featured scan engine that executes a continuously updated and extended feed of Network Vulnerability Tests (NVTs).
OpenVAS SMB provides modules for the OpenVAS Scanner to interface with Microsoft Windows Systems through the Windows Management Instrumentation API and a winexe binary to execute processes remotely on that system.
Build and install openvas-smb;
cd ../../openvas-smb/
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/gvm
make && sudo make installBuild and install OpenVAS scanner;
cd ../../openvas
sed -i.bak 's/-Werror/-Wno-error/' misc/CMakeLists.txt
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/gvm
make
sudo make installIf you get the error below while running the make command;
CMake Error at /opt/gvm/gvm-source/openvas/cmake/GetGit.cmake:33 (string):
string sub-command REPLACE requires at least four arguments.
Call Stack (most recent call first):
/opt/gvm/gvm-source/openvas/cmake/GetGit.cmake:39 (Git_GET_REVISION)The exit as gvm user and run the command below as privileged user;
sudo git config --global --add safe.directory /opt/gvm/gvm-source/openvasThen rerun the compilation and installation command.
Configuring OpenVAS Scanner
The host scan information is stored temporarily on Redis server. The default configuration of Redis server is /etc/redis/redis.conf.
Switch back to privileged user and proceed.
exitTo begin run the command below to create the cache to the installed shared libraries;
ldconfigNext, copy OpenVAS scanner Redis configuration file, redis-openvas.conf, to the same Redis config directory;
cp /opt/gvm/gvm-source/openvas/config/redis-openvas.conf /etc/redis/Update the ownership of the configuration.
chown redis:redis /etc/redis/redis-openvas.confUpdate the path to Redis unix socket on the /etc/openvas/openvas.conf using the db_address parameter as follows;
echo "db_address = /run/redis-openvas/redis.sock" > /etc/openvas/openvas.confNote, the Unix socket path is defined on /etc/redis/redis-openvas.conf file.
chown gvm:gvm /etc/openvas/openvas.confAdd gvm user to redis group;
usermod -aG redis gvmYou can also optimize Redis server itself improve the performance by making the following adjustments;
Increase the value of somaxconn in order to avoid slow clients connections issues.
echo "net.core.somaxconn = 1024" >> /etc/sysctl.confRedis background save may fail under low memory condition. To avoid this, enable memory overcommit (man 5 proc).
echo 'vm.overcommit_memory = 1' >> /etc/sysctl.confReload sysctl variables created above.
sysctl -pTo avoid creation of latencies and memory usage issues with Redis, disable Linux Kernel’s support for Transparent Huge Pages (THP). To easily work around this, create a systemd service unit for this purpose.
cat > /etc/systemd/system/disable_thp.service << 'EOL'
[Unit]
Description=Disable Kernel Support for Transparent Huge Pages (THP)
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/bin/sh -c "echo 'never' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled && echo 'never' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag"
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOL
Reload systemd configurations;
systemctl daemon-reloadStart and enable this service to run on system boot.
systemctl enable --now disable_thpRestart OpenVAS Redis server
systemctl enable --now redis-server@openvasA number of Network Vulnerability Tests (NVTs) require root privileges to perform certain operations. Since openvas is launched from an ospd-openvas process, via sudo, add the line below to sudoers file to ensure that the gvm user used in this demo can run the openvas with elevated rights using passwordless sudo.
echo "gvm ALL = NOPASSWD: /opt/gvm/sbin/openvas" >> /etc/sudoers.d/gvmAlso, enable gvm user to run GSA web application daemon, gsad, with passwordless sudo.
Also, update the secure_path to include the GVM /sbin paths, /opt/gvm/sbin.
sed -i '/secure_path="/s|"$|:/opt/gvm/sbin"|' /etc/sudoersUpdate NVTs
Update Network Vulnerability Tests feed from Greenbone Security Feed/Community Feed using the greenbone-nvt-sync command.
The greenbone-nvt-sync command must not be executed as privileged user root, hence switch back to GVM user we created above and update the NVTs.
Ensure the GVM user can write to /var/lib/openvas/.
chown -R gvm: /var/lib/openvas/Next, update the NVTs as openvas user;
sudo -Hiu gvm greenbone-nvt-syncOnce the update is done, you need to update Redis server with the same VT info from VT files;
sudo openvas --update-vt-infoBuild and Install Greenbone Vulnerability Manager
The Greenbone Vulnerability Manager is the central management service between security scanners and the user clients.
To build and install GVM;
su - gvmcd gvm-source/gvmd
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/opt/gvm/lib/pkgconfig:$PKG_CONFIG_PATH
sed -i.bak 's/-Werror/-Wno-error/' CMakeLists.txt
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/gvm
make
sudo make installSimilarly, if you get the error;
-- Found Git: /usr/bin/git (found version "2.25.1")
fatal: unsafe repository ('/opt/gvm/gvm-source/gvmd' is owned by someone else)
To add an exception for this directory, call:Exit as GVM user and run the command below as privileged user;
sudo git config --global --add safe.directory /opt/gvm/gvm-source/gvmdSwitch back to GVM user and rerun the installation.
Build and Install Greenbone Security Assistant
The Greenbone Security Assistant is the web interface developed for the Greenbone Security Manager
cd ../../gsa
rm -rf build
yarn
yarn buildAll content of the production build can be shipped with every web server. For providing GSA via gsad web server, the files need to be copied into the /usr/local/share/gvm/gsad/web/.
Build and Install Greenbone Security Assistant HTTP server
The Greenbone Security Assistant HTTP Server is the server developed for the communication with the Greenbone Security Manager appliances. It connects to the Greenbone Vulnerability Manager Daemon gvmd to provide a full-featured user interface for vulnerability management.
cd ../gsad
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make
sudo make installNext, copy the web interface configs;
exit[[ -d /usr/local/share/gvm/gsad/web ]] || mkdir -p /usr/local/share/gvm/gsad/webchown -R gvm: /usr/local/share/gvm/gsad/webcp -rp /opt/gvm/gvm-source/gsa/build/* /usr/local/share/gvm/gsad/webKeeping the feeds up-to-date
The gvmd Data, SCAP and CERT Feeds should be kept up-to-date by calling the greenbone-feed-sync script regularly (e.g. via a cron entry):
chown -R gvm: /var/lib/gvm/sudo -Hiu gvm greenbone-feed-sync --type GVMD_DATAsudo -Hiu gvm greenbone-feed-sync --type SCAPsudo -Hiu gvm greenbone-feed-sync --type CERTPlease note: The CERT feed sync depends on data provided by the SCAP feed and should be called after syncing the later.
Consider setting cron jobs to run the nvts, cert and scap data update scripts at your preferred frequency to pull updates from the feed servers.
Next, run the command below to generate certificates gvmd. Server certificates are used for authentication while client certificates are primarily used for authorization. More on man gvm-manage-certs.
/opt/gvm/bin/gvm-manage-certs -aSample command output;
Generated private key in /tmp/tmp.kinSHFrwd1/cakey.pem.
Generated self signed certificate in /tmp/tmp.kinSHFrwd1/cacert.pem.
Installed private key to /var/lib/gvm/private/CA/cakey.pem.
Installed certificate to /var/lib/gvm/CA/cacert.pem.
Generated private key in /tmp/tmp.kinSHFrwd1/serverkey.pem.
Generated certificate request in /tmp/tmp.kinSHFrwd1/serverrequest.pem.
Signed certificate request in /tmp/tmp.kinSHFrwd1/serverrequest.pem with CA certificate in /var/lib/gvm/CA/cacert.pem to generate certificate in /tmp/tmp.kinSHFrwd1/servercert.pem
Installed private key to /var/lib/gvm/private/CA/serverkey.pem.
Installed certificate to /var/lib/gvm/CA/servercert.pem.
Generated private key in /tmp/tmp.kinSHFrwd1/clientkey.pem.
Generated certificate request in /tmp/tmp.kinSHFrwd1/clientrequest.pem.
Signed certificate request in /tmp/tmp.kinSHFrwd1/clientrequest.pem with CA certificate in /var/lib/gvm/CA/cacert.pem to generate certificate in /tmp/tmp.kinSHFrwd1/clientcert.pem
Installed private key to /var/lib/gvm/private/CA/clientkey.pem.
Installed certificate to /var/lib/gvm/CA/clientcert.pem.
Removing temporary directory /tmp/tmp.kinSHFrwd1.
Set the proper ownership of certs files;
chown -R gvm: /var/lib/gvm/{CA,private}Build and Install OSPd and OSPd-OpenVAS
Open Scanner Protocol (OSP) creates a unified interface for different security scanners and makes their control flow and scan results consistently available under the central Greenbone Vulnerability Manager service.
su - gvmexport PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/opt/gvm/lib/pkgconfig:$PKG_CONFIG_PATHcd /opt/gvm/gvm-source/ospd
python3 -m pip install .cd /opt/gvm/gvm-source/ospd-openvas
python3 -m pip install .Running OpenVAS Scanner, GSA and GVM services
In order to make the management of OpenVAS scanner, GSA (WebUI service) and GVM daemon, create systemd service unit files for each of them as follows.
Log out as gvm user and execute the commands below as a privileged user.
exitSource /etc/environment to update the PATH;
source /etc/environmentCreate OpenVAS systemd service
cat > /etc/systemd/system/ospd-openvas.service << 'EOL'
[Unit]
Description=OSPd Wrapper for the OpenVAS Scanner (ospd-openvas)
After=network.target networking.service [email protected] postgresql.service
[email protected]
ConditionKernelCommandLine=!recovery
[Service]
ExecStartPre=-rm -rf /run/gvm/ospd-openvas.pid /run/gvm/ospd-openvas.sock
Type=simple
User=gvm
Group=gvm
RuntimeDirectory=gvm
Environment=PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/opt/gvm/bin:/opt/gvm/sbin:/opt/gvm/.local/bin
ExecStart=/opt/gvm/.local/bin/ospd-openvas \
--pid-file /run/gvm/ospd-openvas.pid \
--log-file /var/log/gvm/ospd-openvas.log \
--lock-file-dir /run/gvm -u /run/gvm/ospd-openvas.sock
RemainAfterExit=yes
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOL
Set proper ownership for logs directory, /var/log/gvm and run time data directory, /run/gvm;
chown -R gvm: /var/log/gvm /run/gvm/Reload systemd service unit configurations.
systemctl daemon-reloadsystemctl start ospd-openvasCheck the status of the service;
systemctl status ospd-openvas● ospd-openvas.service - OSPd Wrapper for the OpenVAS Scanner (ospd-openvas)
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/ospd-openvas.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (exited) since Thu 2022-07-07 04:50:27 UTC; 6s ago
Process: 36289 ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/rm -rf /run/gvm/ospd-openvas.pid /run/gvm/ospd-openvas.sock (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 36290 ExecStart=/opt/gvm/.local/bin/ospd-openvas --pid-file /run/gvm/ospd-openvas.pid --log-file /var/log/gvm/ospd-openvas.log --lock-file-dir /run/gvm -u /ru>
Main PID: 36290 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Tasks: 4 (limit: 4618)
Memory: 25.2M
CGroup: /system.slice/ospd-openvas.service
├─36305 /usr/bin/python3 /opt/gvm/.local/bin/ospd-openvas --pid-file /run/gvm/ospd-openvas.pid --log-file /var/log/gvm/ospd-openvas.log --lock-file-dir /run/g>
└─36307 /usr/bin/python3 /opt/gvm/.local/bin/ospd-openvas --pid-file /run/gvm/ospd-openvas.pid --log-file /var/log/gvm/ospd-openvas.log --lock-file-dir /run/g>
Jul 07 04:50:27 ubuntu20 systemd[1]: Starting OSPd Wrapper for the OpenVAS Scanner (ospd-openvas)...
Jul 07 04:50:27 ubuntu20 systemd[1]: Started OSPd Wrapper for the OpenVAS Scanner (ospd-openvas).
Enable OpenVAS scanner to run on system boot;
systemctl enable ospd-openvasCheck the logs on;
tail -f /var/log/gvm/ospd-openvas.logCreating Systemd Service units for GVM services
When run, the installer creates GVM daemon service unit, /lib/systemd/system/gvmd.service.
Let us modify this service unit file;
cp /lib/systemd/system/gvmd.service{,.bak}
cat > /lib/systemd/system/gvmd.service << 'EOL'
[Unit]
Description=Greenbone Vulnerability Manager daemon (gvmd)
After=network.target networking.service postgresql.service ospd-openvas.service
Wants=postgresql.service ospd-openvas.service
Documentation=man:gvmd(8)
ConditionKernelCommandLine=!recovery
[Service]
Type=forking
User=gvm
Group=gvm
RuntimeDirectory=gvmd
Environment=PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/opt/gvm/bin:/opt/gvm/sbin:/opt/gvm/.local/bin
ExecStart=/opt/gvm/sbin/gvmd --osp-vt-update=/run/gvm/ospd-openvas.sock
Restart=always
TimeoutStopSec=10
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOL
Reload system unit configs and start the services;
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable --now gvmdChecking the status;
systemctl status gvmd● gvmd.service - Greenbone Vulnerability Manager daemon (gvmd)
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/gvmd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2022-07-07 04:55:44 UTC; 4s ago
Docs: man:gvmd(8)
Process: 37170 ExecStart=/opt/gvm/sbin/gvmd --osp-vt-update=/run/gvm/ospd-openvas.sock (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 37181 (gvmd)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 4618)
Memory: 3.2M
CGroup: /system.slice/gvmd.service
└─37181 gvmd: Initializing
Jul 07 04:55:44 ubuntu20 systemd[1]: Starting Greenbone Vulnerability Manager daemon (gvmd)...
Jul 07 04:55:44 ubuntu20 systemd[1]: Started Greenbone Vulnerability Manager daemon (gvmd).
You can restart PostgreSQL as well;
systemctl restart postgresqlCheck the GVMD logs. You should be able to see that
tail -f /var/log/gvm/gvmd.logYou should see that the feeds are updating...
md manage:WARNING:2022-07-07 04h56.34 utc:37220: sqlv: sql_exec_internal failed
md manage:WARNING:2022-07-07 04h56.36 utc:37181: sql_exec_internal: PQexec failed: FATAL: terminating connection due to administrator command
server closed the connection unexpectedly
This probably means the server terminated abnormally
before or while processing the request.
(7)
md manage:WARNING:2022-07-07 04h56.36 utc:37181: sql_exec_internal: SQL: BEGIN;
md manage:WARNING:2022-07-07 04h56.36 utc:37181: sqlv: sql_exec_internal failed
md main:MESSAGE:2022-07-07 04h56.55 utc:37302: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 21.4.6~dev1~git-500ef0c5-stable (GIT revision 500ef0c5-stable) (DB revision 242)
md manage:MESSAGE:2022-07-07 04h56.56 utc:37303: No SCAP database found
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2022-07-07 04h57.01 utc:37303: Setting GnuPG dir to '/var/lib/gvm/gvmd/gnupg'
libgvm util:MESSAGE:2022-07-07 04h57.01 utc:37303: Using OpenPGP engine version '2.2.19'
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.01 UTC:37328: OSP service has different VT status (version 202207061012) from database (version (null), 0 VTs). Starting update ...
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.01 UTC:37329: sync_cert: Updating data from feed
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.01 UTC:37329: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2011.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.01 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2011.xml
md manage:WARNING:2022-07-07 04h57.01 UTC:37327: update_scap: No SCAP db present, rebuilding SCAP db from scratch
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.03 UTC:37329: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2012.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.03 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2012.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.05 UTC:37329: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2008.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.05 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2008.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.05 UTC:37329: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2014.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.05 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2014.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.07 UTC:37329: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2013.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.07 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2013.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.09 UTC:37329: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2015.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.09 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2015.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.11 UTC:37327: update_scap: Updating data from feed
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.11 UTC:37327: Updating CPEs
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.11 UTC:37329: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2009.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.11 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2009.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.15 UTC:37329: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2018.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.15 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2018.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.26 UTC:37329: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2019.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.26 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2019.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.31 UTC:37329: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2022.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.31 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2022.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.35 UTC:37329: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2010.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.35 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2010.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.36 UTC:37329: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2016.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.36 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2016.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.39 UTC:37329: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2017.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.39 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2017.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.42 UTC:37329: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2021.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.42 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2021.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.46 UTC:37329: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2020.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.46 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2020.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.50 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K14.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.53 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K15.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h57.57 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K22.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h58.00 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K19.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h58.01 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K13.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h58.02 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K20.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h58.04 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K17.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h58.09 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K16.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h58.11 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K18.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h58.13 UTC:37329: Updating /var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K21.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h58.15 UTC:37329: SCAP database does not exist (yet), skipping CERT severity score update
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 04h58.15 UTC:37329: sync_cert: Updating CERT info succeeded.
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 05h02.59 UTC:37327: Updating /var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2020.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 05h06.32 UTC:37327: Updating /var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2022.xml
...
Creating Systemd Service units for GSA services
When run, the installer creates GSA daemon service unit, /lib/systemd/system/gsad.service.
Let us modify this service unit file;
cp /lib/systemd/system/gsad.service{,.bak}
cat > /lib/systemd/system/gsad.service << 'EOL'
[Unit]
Description=Greenbone Security Assistant daemon (gsad)
Documentation=man:gsad(8) https://www.greenbone.net
After=network.target gvmd.service
Wants=gvmd.service
[Service]
Type=simple
User=gvm
Group=gvm
RuntimeDirectory=gsad
PIDFile=/run/gsad/gsad.pid
Environment=PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/opt/gvm/bin:/opt/gvm/sbin:/opt/gvm/.local/bin
ExecStart=/usr/bin/sudo /usr/local/sbin/gsad -k /var/lib/gvm/private/CA/clientkey.pem -c /var/lib/gvm/CA/clientcert.pem
RemainAfterExit=yes
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOL
The option, -k /var/lib/gvm/private/CA/clientkey.pem -c /var/lib/gvm/CA/clientcert.pem, is as per the certificates path generated by running the gvm-manage-certs command above.
Enable GVM user to run gsad with sudo rights;
echo "gvm ALL = NOPASSWD: $(which gsad)" >> /etc/sudoers.d/gvmReload system unit configs and start the services;
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable --now gsadChecking the status;
systemctl status gsad
● gsad.service - Greenbone Security Assistant daemon (gsad)
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/gsad.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (exited) since Thu 2022-07-07 18:56:01 UTC; 33s ago
Docs: man:gsad(8)
https://www.greenbone.net
Process: 36900 ExecStart=/usr/bin/sudo /usr/local/sbin/gsad -k /var/lib/gvm/private/CA/clientkey.pem -c /var/lib/gvm/CA/clientcert.pem (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 36900 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Tasks: 4 (limit: 2281)
Memory: 3.4M
CGroup: /system.slice/gsad.service
├─36915 /usr/local/sbin/gsad -k /var/lib/gvm/private/CA/clientkey.pem -c /var/lib/gvm/CA/clientcert.pem
└─36916 /usr/local/sbin/gsad -k /var/lib/gvm/private/CA/clientkey.pem -c /var/lib/gvm/CA/clientcert.pem
Jul 07 18:56:01 ubuntu20 systemd[1]: Started Greenbone Security Assistant daemon (gsad).
Jul 07 18:56:01 ubuntu20 sudo[36900]: gvm : TTY=unknown ; PWD=/ ; USER=root ; COMMAND=/usr/local/sbin/gsad -k /var/lib/gvm/private/CA/clientkey.pem -c /var/lib/gvm/CA>
Jul 07 18:56:01 ubuntu20 sudo[36900]: pam_unix(sudo:session): session opened for user root by (uid=0)
Jul 07 18:56:04 ubuntu20 sudo[36912]: Oops, secure memory pool already initialized
Jul 07 18:56:04 ubuntu20 sudo[36900]: pam_unix(sudo:session): session closed for user root
Check the logs;
tail -f /var/log/gvm/gsad.logCreate GVM Scanner
Since we launched the scanner and set it to use our non-standard scanner host path (/run/gvm/ospd-openvas.sock), we need to create and register our scanner;
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --create-scanner="Kifarunix-demo OpenVAS Scanner" \
--scanner-type="OpenVAS" --scanner-host=/run/gvm/ospd-openvas.sockcommand output;
Scanner created.Next, you need to verify your scanner. For this, you first need to get the scanner identifier;
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --get-scanners08b69003-5fc2-4037-a479-93b440211c73 OpenVAS /run/ospd/ospd-openvas.sock 0 OpenVAS Default
6acd0832-df90-11e4-b9d5-28d24461215b CVE 0 CVE
17597043-78cb-492c-b7b4-3b4b36406ed1 OpenVAS /run/gvm/ospd-openvas.sock 9390 Kifarunix-demo OpenVAS ScannerBased on the output above, our scanner UUID is, 17597043-78cb-492c-b7b4-3b4b36406ed1.
Verify the scanner;
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --verify-scanner=17597043-78cb-492c-b7b4-3b4b36406ed1Command output;
Scanner version: OpenVAS 21.4.5~dev1~git-773a6537-stable.Create GVM Admin User
Create GVM administrative user by running the command below;
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --create-user adminThis command generates a random password for the user. See sample output below;
User created with password '3ae45864-0d6a-4a53-938f-730a1bb5d959'.If you want to create a user and at the same time create your own password;
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --create-user USERNAME --password=PASSWORDOtherwise, you can reset the password of an already existing user;
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --user=<USERNAME> --new-password=<PASSWORD>An administrator user can later create further users or administrators via clients like the Greenbone Security Assistant (GSA).
Set the Feed Import Owner
According to gvmd/INSTALL.md, certain resources that were previously part of the gvmd source code are now shipped via the feed. An example is the config “Full and Fast”.
gvmd will only create these resources if a “Feed Import Owner” is configured:
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --modify-setting 78eceaec-3385-11ea-b237-28d24461215b --value <uuid_of_user>The UUIDs of all created users can be found using
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --get-users --verboseSample output;
admin 2dd752e3-a051-44c6-b214-079673a263f7Then modify the gvmd settings with the user UUID.
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --modify-setting 78eceaec-3385-11ea-b237-28d24461215b --value 2dd752e3-a051-44c6-b214-079673a263f7Accessing GVM 21.4 Web Interface
Greenbone Security Assistant (GSA) WebUI daemon opens port 443 and listens on all interfaces.
ss -altnp | grep 443LISTEN 0 128 *:443 *:* users:(("gsad",pid=37710,fd=10))If firewall is running, open this port to allow external access.
ufw allow 443/tcpYou can now access GSA via the url https:<serverIP-OR-hostname>.
Accept the self-signed SSL warning and proceed.
You can now access GSA via the url https:<serverIP-OR-hostname>. Accept the self-signed SSL warning and proceed.
Login with the administrative credentials generated above.
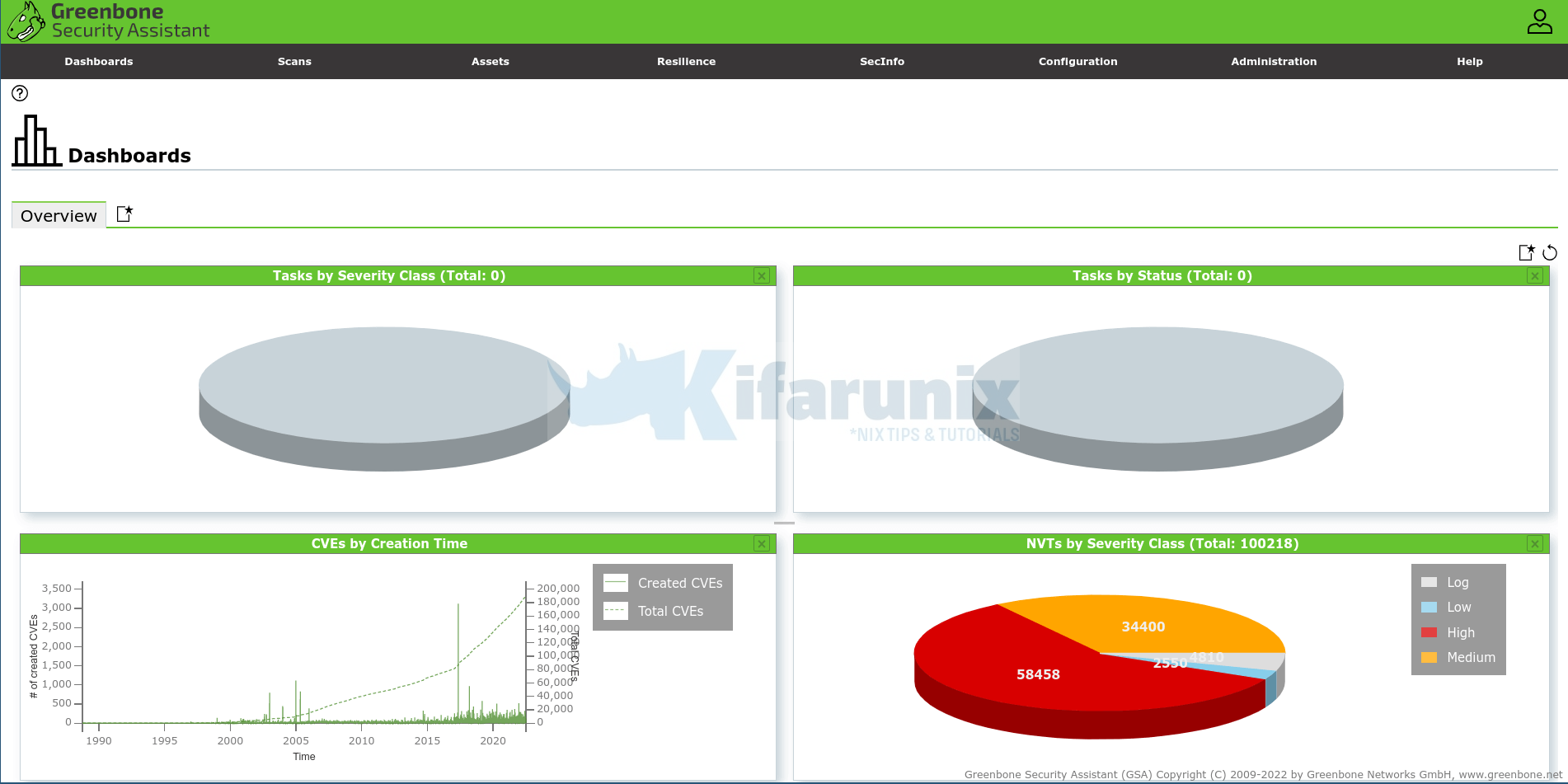
Dashboard;
SecInfo
It may take sometime to update the database with SCAP data and you may see No SCAP database found on the dashboard. Be sure to check the logs to confirm that actually the database is being updated;
tail -f /var/log/gvm/gvmd.log
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 05h25.00 utc:38216: Modifying setting.
md manage:MESSAGE:2022-07-07 05h25.00 utc:38216: No SCAP database found
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 05h27.55 UTC:37327: Updating /var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2005.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 05h28.36 UTC:37327: Updating /var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2004.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 05h28.52 UTC:37327: Updating /var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2010.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 05h30.19 UTC:37327: Updating /var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2012.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 05h31.06 UTC:37327: Updating /var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2009.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 05h31.55 UTC:37327: Updating /var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2015.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 05h33.00 UTC:37327: Updating /var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2013.xml
md manage: INFO:2022-07-07 05h33.38 UTC:37327: Updating /var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2018.xml
...
And there you go. That is all it take to install and Setup GVM 21.4 on Ubuntu 20.04. You can now start running your scans.
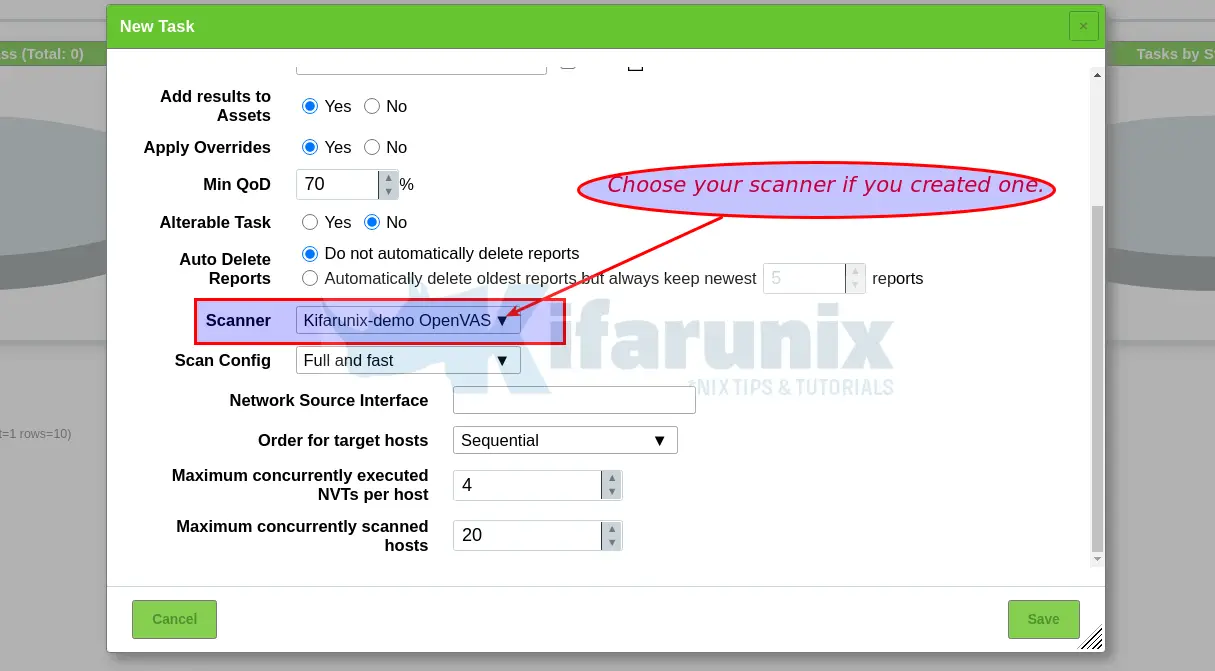
NOTE: When creating a scan task, be sure to select the Scanner we created above.
You can now create your target hosts to scan and schedule the scans to run at your own preferred time.
That marks the end of our tutorial on how to install and setup GVM 21.4 on Ubuntu 20.04.
Reference
Source files README.md and INSTALL.md files
Other Tutorials


at the time of -》 Configuring OpenVAS Scanner 《-
print “bash: /etc/openvas/openvas.conf: No such file or directory”
Cannot continue,help
Ensure that build and install of openvas completed successfully.
‘Update NVTs’
sudo openvas –update-vt-info
openvas: error while loading shared libraries: libopenvas_nasl.so.21: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/gvm
— Looking for paho-mqtt3c … LIBPAHO-NOTFOUND
CMake Error at util/CMakeLists.txt:57 (message):
libpaho-mqtt3c is required for MQTTv5 support.
Amazing tuto! thank you very much.